1. CPU加压工具
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#define __USE_GNU
#include <sched.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define INTERVAL 100
/*
**
* gcc -D__USE_GNU -o consume_cpu consume_cpu.c -lpthread
* Usage: ./consume_cpu [<cpu utilization percent>]
**
*/
struct consume_inf{
int cpu;
int percent;
};
double get_time(){
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return (tv.tv_sec*1000+tv.tv_usec*1.0/1000);
}
void* consume_thread(void *arg){
struct consume_inf *inf;
inf = (struct consume_inf *)arg;
int cpu = inf->cpu;
int percent = inf->percent;
cpu_set_t mask;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(cpu, &mask);
if(pthread_setaffinity_np(pthread_self(), sizeof(mask), &mask) == -1){
printf("set affinity failed..");
}
int busy_span = percent;
int idle_span = INTERVAL - percent;
double start_time;
while(1){
start_time = get_time();
while((get_time()-start_time) <= percent);
usleep(idle_span*1000);
}
}
int main( int argc, char *argv[]){
int num = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_CONF);
int i = 0;
pthread_t ptid[1000];
if(argc < 2){
printf("usage: %s [<cpu utilization percent>]\n", argv[0]);
printf("error: cpu utilization percent is a required parameter.\n");
printf("for example: %s 80\n", argv[0]);
return(-2);
}
int percent = atoi(argv[1]);
struct consume_inf inf[1000];
for(i = 0; i < num; i++){
inf[i].cpu = i;
inf[i].percent = percent;
if(pthread_create(&ptid[i], NULL, consume_thread, &(inf[i]))){
printf("Create pthread (%d) Error.\n", i);
return(-1);
}
}
for(i = 0; i < num; i++){
pthread_join(ptid[i], NULL);
}
return(0);
}
Linux下编译方法:
gcc -D__USE_GNU -o consume_cpu consume_cpu.c -lpthread
使用方法:./consume_cpu [<cpu utilization percent>],例如:./consume_cpu 80,CPU整体利用率将保持在80%左右。
2. 内存加压工具
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/sysinfo.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#define DEVIATION 100 //允许误差为 DEVIATION 兆
/*
**
* gcc -o consume_mem consume_mem.c
* Usage: ./consume_mem [<ram utilization percent>]
**
*/
typedef struct consume_inf{
void* memAddr;
struct consume_inf *next;
}ramlink; //抢占内存链表
void* consume_1M_ram(){
return malloc(1 << 20);
}
int main( int argc, char *argv[] ){
if(argc < 2){
printf("usage: %s [<ram utilization percent>]\n", argv[0]);
printf("error: ram utilization percent is a required parameter.\n");
printf("for example: %s 80\n", argv[0]);
return(-2);
}
int percent = atoi(argv[1]);
int bs_count = 0;
struct sysinfo si;
sysinfo(&si);
unsigned long totalram = si.totalram;
unsigned long targetfree = totalram / 100 * (100 - percent);
unsigned long nowfree = si.freeram;
ramlink *head = NULL;
while(1){
sysinfo(&si);
nowfree = si.freeram;
int perc_now = (totalram - nowfree) * 100 / totalram;
printf("Current ram utilization is %d%%, I am holding %dMB.\n", perc_now, bs_count);
//多吃了内存,释放内存
if(targetfree > nowfree && (targetfree - nowfree) > DEVIATION * 1024 * 1024 && head != NULL){
unsigned long tofree_m = (targetfree - nowfree) / 1024 / 1024;
int j = 0;
printf("To release %luMB ram...\n", tofree_m);
for(j = 0; j < tofree_m; j++){
if(head == NULL){
printf("All memory(%dMB) has been released.\n", j);
break;
}
ramlink *p = head->next;
free(head->memAddr);
free(head);
head = p;
bs_count--;
}
}
//少吃了内存,继续吃内存
if(nowfree > targetfree && (nowfree - targetfree) > DEVIATION * 1024 * 1024){
unsigned long eatram_m = (nowfree - targetfree) / 1024 / 1024;
int i = 0;
printf("To preempt %luMB ram...\n", eatram_m);
for(i = 0; i < eatram_m; i++){
ramlink *p = (ramlink*)malloc(sizeof(ramlink));
if(p == NULL) break;
p->memAddr = consume_1M_ram();
if(p->memAddr == NULL){
free(p);
break;
}
memset(p->memAddr, 0, 1 << 20);
p->next = head;
head = p;
bs_count++;
}
}
sleep(10);
}
return 0;
}
Linux下编译方法:
gcc -o consume_mem consume_mem.c
使用方法:./consume_mem [<ram utilization percent>],例如:./consume_mem 80,内存利用率将保持在80%左右。
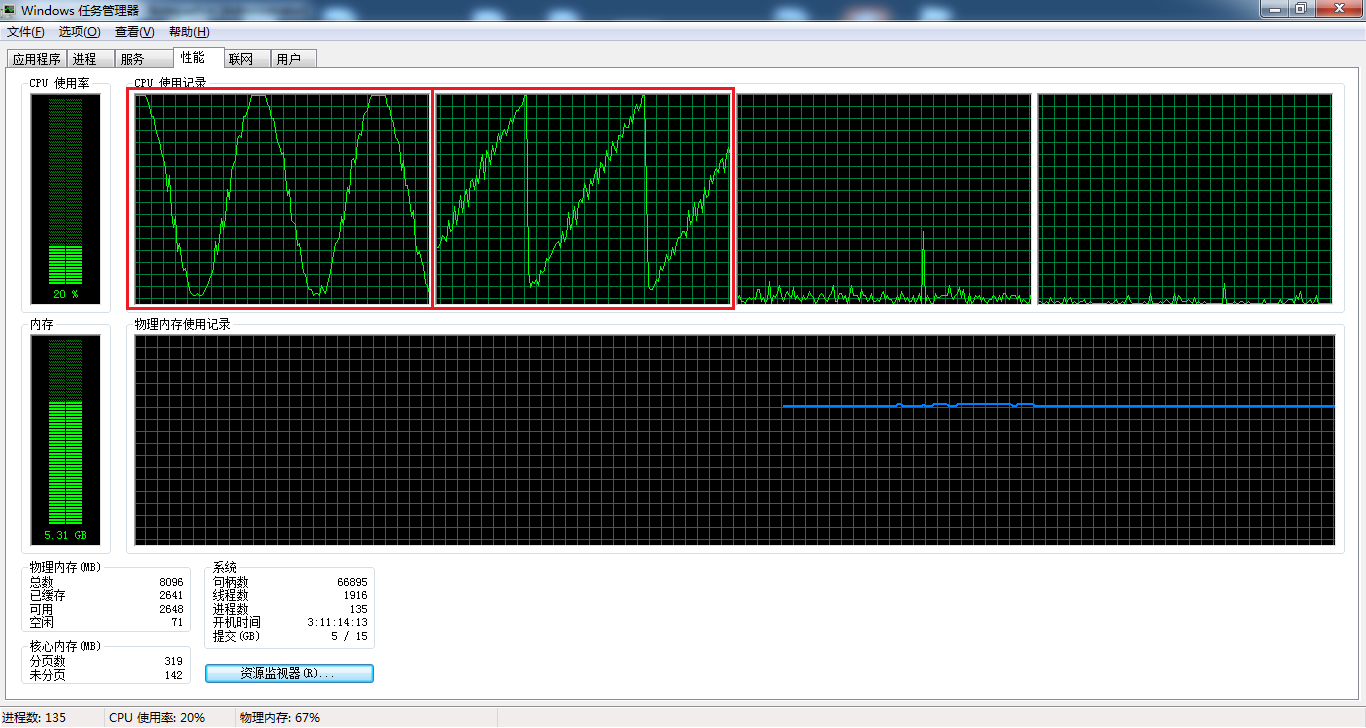
3. 关联实验
将CPU利用率控制为正弦波和锯齿波。
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define COUNT 200
const double SPLIT = 0.01;
const double PI = 3.14159265;
const double SLOPE = 150;
const int INTERVAL = 300;
DWORD WINAPI SineThread(LPVOID Sine)
{
DWORD busySpan[COUNT];
DWORD idleSpan[COUNT];
int half = INTERVAL/2;
double radian = 0.0;
DWORD startTime;
int i;
for (i=0; i<COUNT; i++)
{
busySpan[i] = (DWORD)(half + half*sin(PI*radian));
idleSpan[i] = (DWORD)(INTERVAL - busySpan[i]);
radian += SPLIT;
}
i = 0;
while(1)
{
i %= COUNT;
startTime = GetTickCount();
while((GetTickCount()-startTime) <= busySpan[i])
;
Sleep(idleSpan[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
DWORD WINAPI SawThread(LPVOID Saw)
{
DWORD busySpan[COUNT];
DWORD idleSpan[COUNT];
int half = INTERVAL/2;
double radian = 0.0;
DWORD startTime;
int i;
for (i=0; i<COUNT; i++)
{
busySpan[i] = (DWORD)(SLOPE*radian);
idleSpan[i] = (DWORD)(INTERVAL - busySpan[i]);
radian += SPLIT;
}
i = 0;
while(1)
{
i %= COUNT;
startTime = GetTickCount();
while((GetTickCount()-startTime) <= busySpan[i])
;
Sleep(idleSpan[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
HANDLE hThread1, hThread2;
DWORD dwThreadId1, dwThreadId2;
hThread1 = CreateThread(NULL, 0, SineThread, 0, CREATE_SUSPENDED, &dwThreadId1);
hThread2 = CreateThread(NULL, 0, SawThread, 0, CREATE_SUSPENDED, &dwThreadId2);
SetThreadAffinityMask(hThread1, 1);
SetThreadAffinityMask(hThread2, 2);
ResumeThread(hThread1);
ResumeThread(hThread2);
SuspendThread(GetCurrentThread());
return 0;
}